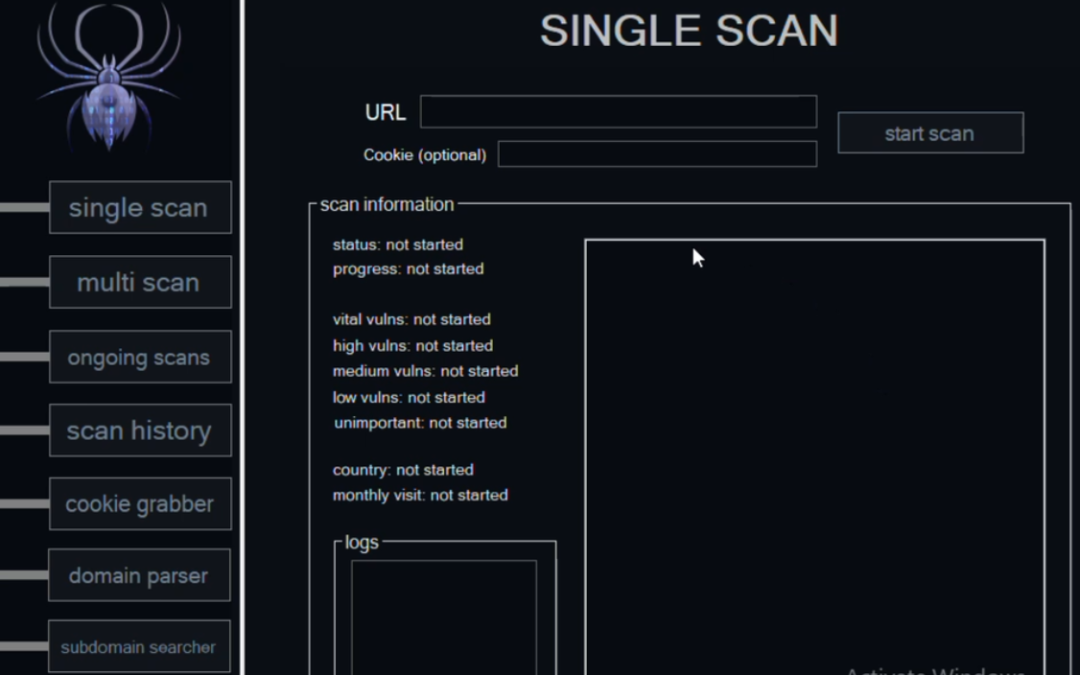
Cybercriminals are selling hundreds of thousands of credential sets stolen with the help of a cracked version of Acunetix, a powerful commercial web app vulnerability scanner, new research finds. The cracked software is being resold as a cloud-based attack tool by at least two different services, one of which KrebsOnSecurity traced to an information technology firm based in Turkey.
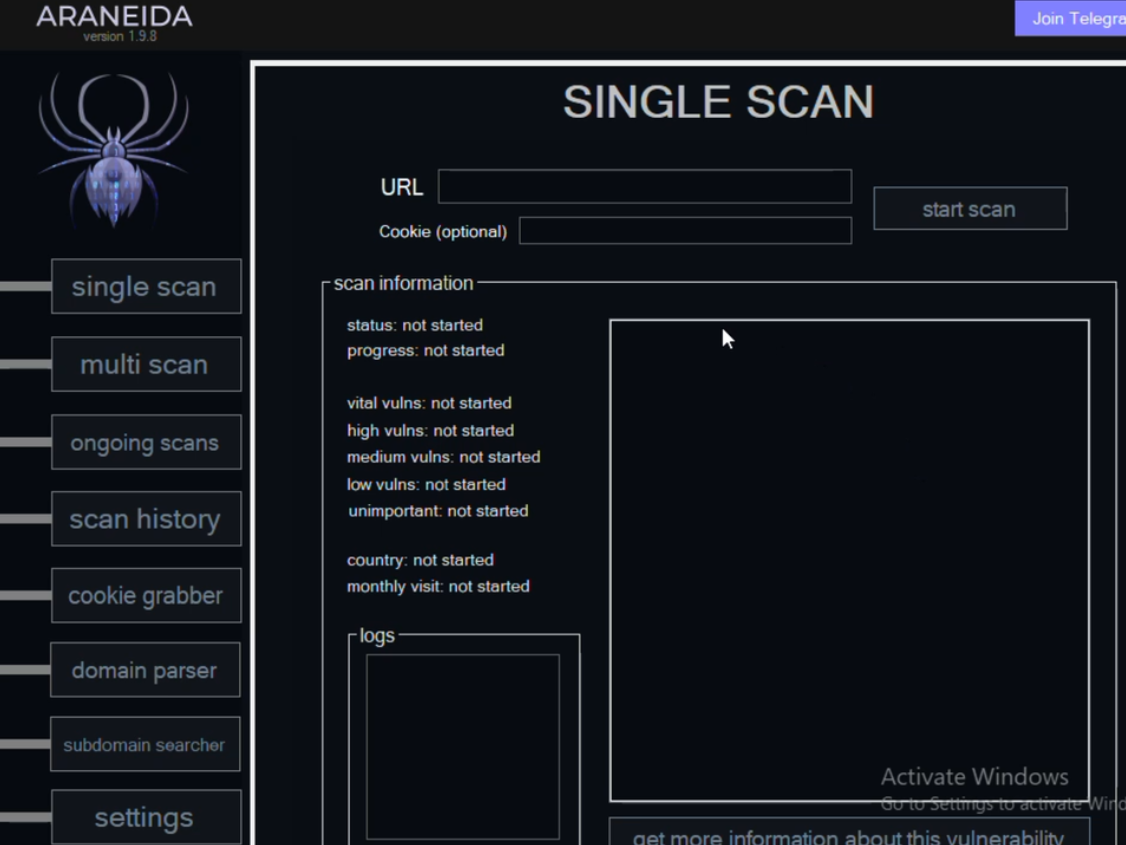
Araneida Scanner.
Cyber threat analysts at Silent Push said they recently received reports from a partner organization that identified an aggressive scanning effort against their website using an Internet address previously associated with a campaign by FIN7, a notorious Russia-based hacking group.
But on closer inspection they discovered the address contained an HTML title of “Araneida Customer Panel,” and found they could search on that text string to find dozens of unique addresses hosting the same service.
It soon became apparent that Araneida was being resold as a cloud-based service using a cracked version of Acunetix, allowing paying customers to conduct offensive reconnaissance on potential target websites, scrape user data, and find vulnerabilities for exploitation.
Silent Push also learned Araneida bundles its service with a robust proxy offering, so that customer scans appear to come from Internet addresses that are randomly selected from a large pool of available traffic relays.
The makers of Acunetix, Texas-based application security vendor Invicti Security, confirmed Silent Push’s findings, saying someone had figured out how to crack the free trial version of the software so that it runs without a valid license key.
“We have been playing cat and mouse for a while with these guys,” said Matt Sciberras, chief information security officer at Invicti.
Silent Push said Araneida is being advertised by an eponymous user on multiple cybercrime forums. The service’s Telegram channel boasts nearly 500 subscribers and explains how to use the tool for malicious purposes.
In a “Fun Facts” list posted to the channel in late September, Araneida said their service was used to take over more than 30,000 websites in just six months, and that one customer used it to buy a Porsche with the payment card data (“dumps”) they sold.
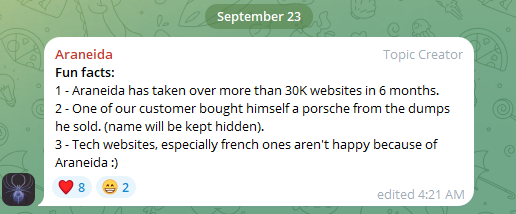
Araneida Scanner’s Telegram channel bragging about how customers are using the service for cybercrime.
“They are constantly bragging with their community about the crimes that are being committed, how it’s making criminals money,” said Zach Edwards, a senior threat researcher at Silent Push. “They are also selling bulk data and dumps which appear to have been acquired with this tool or due to vulnerabilities found with the tool.”
Silent Push also found a cracked version of Acunetix was powering at least 20 instances of a similar cloud-based vulnerability testing service catering to Mandarin speakers, but they were unable to find any apparently related sales threads about them on the dark web.
Rumors of a cracked version of Acunetix being used by attackers surfaced in June 2023 on Twitter/X, when researchers first posited a connection between observed scanning activity and Araneida.
According to an August 2023 report (PDF) from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Acunetix (presumably a cracked version) is among several tools used by APT 41, a prolific Chinese state-sponsored hacking group.
THE TURKISH CONNECTION
Silent Push notes that the website where Araneida is being sold — araneida[.]co — first came online in February 2023. But a review of this Araneida nickname on the cybercrime forums shows they have been active in the criminal hacking scene since at least 2018.
A search in the threat intelligence platform Intel 471 shows a user by the name Araneida promoted the scanner on two cybercrime forums since 2022, including Breached and Nulled. In 2022, Araneida told fellow Breached members they could be reached on Discord at the username “Ornie#9811.”
According to Intel 471, this same Discord account was advertised in 2019 by a person on the cybercrime forum Cracked who used the monikers “ORN” and “ori0n.” The user “ori0n” mentioned in several posts that they could be reached on Telegram at the username “@sirorny.”
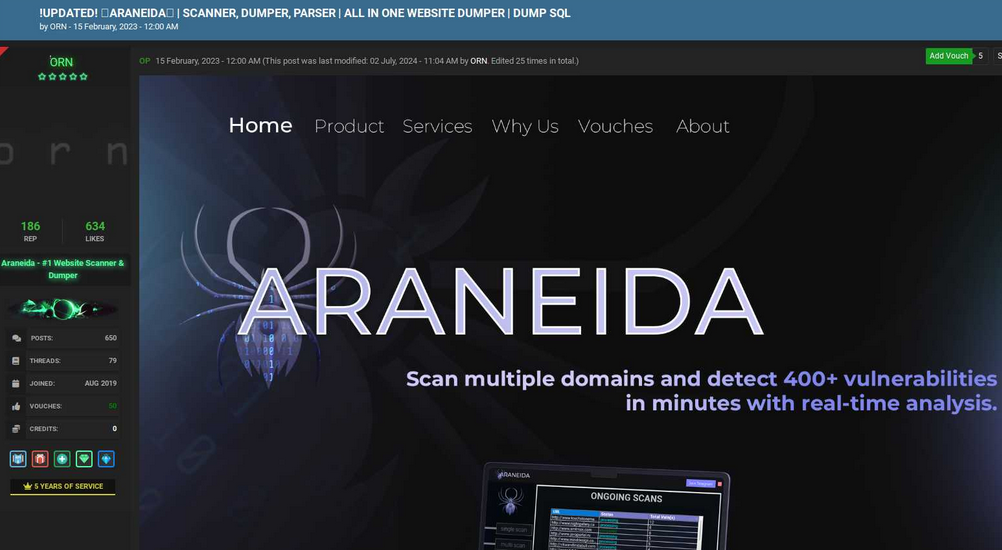
Orn advertising Araneida Scanner in Feb. 2023 on the forum Cracked. Image: Ke-la.com.
The Sirorny Telegram identity also was referenced as a point of contact for a current user on the cybercrime forum Nulled who is selling website development services, and who references araneida[.]co as one of their projects. That user, “Exorn,” has posts dating back to August 2018.
In early 2020, Exorn promoted a website called “orndorks[.]com,” which they described as a service for automating the scanning for web-based vulnerabilities. A passive DNS lookup on this domain at DomainTools shows that its email records pointed to the address ori0nbusiness@protonmail.com.
Constella Intelligence, a company that tracks information exposed in data breaches, finds this email address was used to register an account at Breachforums in July 2024 under the nickname “Ornie.” Constella also finds the same email registered at the website netguard[.]codes in 2021 using the password “ceza2003” [full disclosure: Constella is currently an advertiser on KrebsOnSecurity].
A search on the password ceza2003 in Constella finds roughly a dozen email addresses that used it in an exposed data breach, most of them featuring some variation on the name “altugsara,” including altugsara321@gmail.com. Constella further finds altugsara321@gmail.com was used to create an account at the cybercrime community RaidForums under the username “ori0n,” from an Internet address in Istanbul.
According to DomainTools, altugsara321@gmail.com was used in 2020 to register the domain name altugsara[.]com. Archive.org’s history for that domain shows that in 2021 it featured a website for a then 18-year-old Altuğ Şara from Ankara, Turkey.

Archive.org’s recollection of what altugsara dot com looked like in 2021.
LinkedIn finds this same altugsara[.]com domain listed in the “contact info” section of a profile for an Altug Sara from Ankara, who says he has worked the past two years as a senior software developer for a Turkish IT firm called Bilitro Yazilim.
Neither Altug Sara nor Bilitro Yazilim responded to requests for comment.
Invicti’s website states that it has offices in Ankara, but the company’s CEO said none of their employees recognized either name.
“We do have a small team in Ankara, but as far as I know we have no connection to the individual other than the fact that they are also in Ankara,” Invicti CEO Neil Roseman told KrebsOnSecurity.
Researchers at Silent Push say despite Araneida using a seemingly endless supply of proxies to mask the true location of its users, it is a fairly “noisy” scanner that will kick off a large volume of requests to various API endpoints, and make requests to random URLs associated with different content management systems.
What’s more, the cracked version of Acunetix being resold to cybercriminals invokes legacy Acunetix SSL certificates on active control panels, which Silent Push says provides a solid pivot for finding some of this infrastructure, particularly from the Chinese threat actors.
Further reading: Silent Push’s research on Araneida Scanner.